Theme: Investigating the Current Novelty & Core Approaches in Kidney Disorders and Nephrology
Kidney Meet 2020
Dear Potential Researchers, Scientists, Industrialists & Students,
Join us for 5th World Kidney Congress
Update your skills, Meet your academic heroes, Engage in high-level debates and refine your ideas enhance your knowledge base, and broaden your horizons, Visit a new place and have fun, - all in one place!
Date: June 22-23, 2020
Webinar
If you are interested to be a part of this event as a speaker or delegate!
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +447723584377
Kidney Meet 2020 is an integration of the science, theory and clinical information for the aim of analysing, decoding and to minimize kidney-based distress or dysfunction and to promote individual health and private development. Kidney Meet 2020 Conference invites all the renowned scientists, Nephrologists, Kidney Specialists, General Physicians, Primary Health Care Specialists, Pharmaceutical Industrial Delegates, Talented Young Scientists and Student communities from worldwide to attend World Kidney Congress under a single roof where investigators across the globe can meet, network, perceive and present new scientific innovations.
Why to attend Kidney Meet 2020 Conference?
Kidney Meet 2020 Highlights of the theme "Investigating the Current Novelty & Core Approaches in Kidney Disorders and Nephrology" which basically focus on the most recent advancements in aversion and treatment of different kidney disorders. With members from around the world focused on learning about nephrology and its advances; this is the best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the nephrology community This global event will be an excellent opportunity for the Nephrologists and alternative practitioners to encourage the profound administration of kidney medication and gives strong talks on Novel techniques and procedures identified with current novelty and the recent approaches of kidney and as well as exploring new thoughts and ideas for treatment of kidney complications.
Conference Highlights of Kidney Meet 2020 Conference:
- Nephrology
- Kidney Disorders
- Pediatric Nephrology
- Geriatric Nephrology
- Clinical Nephrology
- Hereditary Kidney Diseases
- Dialysis
- Urology & Urinary Tract Infections
- Onconephrology and Nephritis
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Kidney and Bladder stones
- Surgery for Renal Disease
- Biomarkers of Kidney Diseases
- Cardiovascular Impacts of Kidney Diseases
- Stem Cells in Renal Disorders
- Renal Nutrition and Metabolism
- Glomerular Disorders
- Renal Replacement Therapy
- Kidney Transplantation
- Nephrology Diagnosis And Treatment
Target Audiences of Kidney Meet 2020 Conference:
- Nephrologists
- Kidney Specialists
- General Physicians
- Nephrology and Urology Professors
- Renal Practitioners
- Kidney Coordinators
- Renal Transplantation Surgeons
- Postdoctoral Students
- Nephrology Academicians
- Renal Dieticians
- Young Research Scientists
- Business Delegates
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Laboratory Technicians and Diagnostic Companies
- Pharmaceutical Companies and Industries
- Nephrology and Urology Associations and Societies
- Medical & Pharmaceutical Companies
Track-1: Nephrology
Nephrology is the kind of medicine and pediatric medicine which concerns itself with the kidneys: the study of normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of renal disorder, from diet and medicine to nephritic replacement medical aid. Nephrology conjointly studies general conditions that have an effect on the kidneys, like polygenic disease and reaction disease; and general diseases that occur as a result of renal disorder, like nephritic osteodystrophy and hypertension. The kidneys serve important functions, including filtration and excretion of metabolic waste products (urea and ammonium); regulation of necessary electrolytes, fluid, acid-base balance and stimulation of red blood cell production. They conjointly serve to manage pressure via the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, dominant organic process of water and maintaining intravascular volume. The kidneys conjointly absorb aldohexose and amino acids and have secretion functions via glycoprotein, calcitriol and cholecarciferol activation.
-
Nephrology & renal Studies
-
Renal histopathology
-
Advances in nephrology
-
Artificial kidney
-
Pelvic kidney
Track-2: Kidney Disorders
Kidney diseases also called nephropathy or renal infection cause harm to kidney. Nephritis is inflammatory kidney infection whereas nephrosis is non-inflammatory kidney diseases. Kidney diseases sometimes have an effect on renal failure and urinary organ harm. Acute kidney injury, once referred to as acute renal failure could be a syndrome that is characterized by the speedy loss of the kidney's excretory function and is often diagnosed by the accumulation of end products of nitrogen metabolism (Urea and creatinine) or decreased urine output, or both. Chronic kidney disease also called as chronic kidney failure which describes the gradual loss of kidney function. It includes complications like high blood pressure, anemia (low blood count), weak bones, poor nutritional health and nerve damage. Kidney disease can also increase the risk of heart and blood vessel disease.
-
Nephrosis
-
Acute renal failure
-
Glomerulonephritis
-
Polycystic kidney disease
-
Acquired cystic kidney disease
-
Reflux nephropathy
-
Azotemia
-
Uremia
-
Uremic Encephalopathy
Track-3: Pediatric Nephrology
The study of pediatric nephrology determines diagnosis and management of infants with a chronic and acute kidney disorders. The division of pediatric nephrology assesses and treats hypertension, hematuria, proteinuria, renal tubular acidosis, nephrolithiasis, glomerulonephritis and kidney damage in children. It additionally includes complete care to medical specialty patients with finish stage excretory organ syndromes, together with thought to patients experiencing serosa qualitative analysis, hemodialysis and excretory organ transplantation in infants. The division of medical specialty medical specialty evaluates and treats high blood pressure, hematuria, proteinuria, renal rounded acidosis, nephrolithiasis, glomerulonephritis and kidney harm in kids. It likewise incorporates total thought to medical specialty patients with finish organize excretory organ disorders, together with thought to patients encountering serosa qualitative analysis, hemodialysis and excretory organ transplantation in newborn youngsters.
-
Pediatric renal failure
-
Pediatric kidney dialysis
-
Pediatric chronic hemodialysis
-
Pediatric renal transplantation
-
Advances in pediatric kidney operation
Track-4: Geriatric Nephrology
Geriatric Nephrology is the branch of medication or general medicine and geriatric medicine deals with diseases of the excretory organ. Patients who are living longer may acquire diseases that accelerate chronic kidney disease, which often remains undetected until patients are confronted with the sudden need for dialysis. Geriatric Nephrology aims to study of assess the clinical efficacy of total and regional bone densitometry in a large Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) populace and to determine the clinical, biological and radiographic variables that best acknowledged osteopenia CAPD patients. Patients who are living longer may acquire contaminations that stimulate ceaseless kidney sicknesses, which routinely stay undetected until the point that patients are resisted with the sudden prerequisite for dialysis. Renal cystic disease incorporates a broad assortment of ailment components.
-
Interstitial nephritis
-
Clinical renal densitometry
-
Biomarkers in nephrology
-
Renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis
Track-5: Clinical Nephrology
Clinical nephrology involves medical treatment of urinary organ diseases and conditions. This may entail working with other areas of the body that also are influenced by the kidneys. Kidney issues will cause solution imbalances within the blood, leading to serious symptoms as well as excess fluid within the tissues, mental confusion or irregular heartbeat. Clinical medicine can also facilitate patients United Nations agency have high force per unit area, as a result of high blood pressure are often damaging to the kidneys. Patients are referred to clinical nephrology doctors after a urinalysis, for different reasons, such as acute kidney failure, hematuria, proteinuria, chronic kidney diseases, kidney stones, hypertension, and disarranges of acid/base or electrolytes.
-
Critical care nephrology
-
Stem cell and regenerative nephrology
-
Oncologic nephrology
-
Obstructive nephropathy
Track-6: Hereditary Kidney Diseases
Hereditary kidney disorders represent significant risk for the development of end stage renal disease (ESRD). Most of them are recognized in childhood, or prenatal particularly those phenotypically expressed as anomalies on ultrasound examination (US) during pregnancy. Some kidney diseases result from genetic factors. Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD), for example, is a genetic disorder in which many cysts grow in the kidneys. PKD cysts will slowly switch a lot of the mass of the kidneys, decreasing urinary organ perform and resulting in failure. Some urinary organ complications might show up even before birth. Examples contain autosomal recessive PKD (ARPKD) a rare form of PKD, and other developing problems that interfere with the normal formation of the nephrons. The signs of kidney disease in children vary.
-
Polycystic kidney disease
-
Medullary sponge kidney
-
Bartter syndrome
-
Alport syndrome
-
Horseshoe kidney
-
Nephronophthisis
-
Tuberous sclerosis
Track-7: Dialysis
Dialysis performs the function of the kidneys if they’ve failed. It is a treatment that filters and purifies the blood using a machine. This helps keep the fluids and electrolytes in balance when the kidneys can’t do their job. Dialysis, the additional common variety of kidney-replacement medical aid, could be a manner of improvement the blood with a synthetic excretory organ. There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Hemodialysis: It is a system of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not running commonly and is the choice of renal replacement remedy for patient who need dialysis acutely and for many patients as preservation therapy. There are three styles of hemodialysis: Conventional hemodialysis, each day hemodialysis, and Nocturnal hemodialysis.
Peritoneal Dialysis: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a remedy that uses the liner of your stomach (stomach area), called your peritoneum, and a cleaning answer referred to as dialysate to smooth your blood. The two maximum not unusual styles of PD are Non-stop ambulatory PD (CAPD) and Non-stop cycler-assisted PD (CCPD).
-
Hemodialysis
-
Peritoneal dialysis
-
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
-
Continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis
-
Intermittent peritoneal dialysis
Track-8: Urology & Urinary Tract Infections
Urology also referred to as genitourinary surgical procedure, is a branch of medication that focuses on surgical and medical sicknesses of the urinary tract system and an infection in any part of the urinary device, is referred to as a urinary tract infection. A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, the ureters, the bladder or the urethra. Most infections are in the bladder or the urethra, the parts of the urinary tract that are closest to the outside of the body. An infection can occur in either the upper or lower urinary tract. Further common in adults than children, urinary tract infections are second only to respiratory infections as the most common type of infection.
-
Cystitis
-
Pyelonephritis
-
Urethritis
-
Cancers of the kidney and genitourinary tract
-
Stress urinary incontinence
-
Urothelial tumours
Track-9: Onconephrology and Nephritis
Onco-nephrology is a subspecialty of Nephrology which treats kidney diseases. Randomized controlled preliminaries in a very subspecialty like onconephrology should be conceivable once there's a joint effort among nephrologists and malignancy doctors from malignant growth bases on the globe that connect and share explore thoughts at worldwide gatherings. Nephritis is irritation of the urinary organ the foremost vital predominant to intense nephritis is glomerulonephritis. Pyelonephritis effects in grown-ups quite kids and it's perceived as irritation of the urinary organ and higher tract. The third sort of nephritis is genetic nephritis, an uncommon acquired condition.
-
Paraneoplastic glomerulonephritis
-
Amyloidosis
-
Renal cell carcinoma and types
-
Urinalysis
-
Prostate cancer
-
Tuberous sclerosis
Track-10: Diabetic Nephropathy
High blood glucose, also called blood sugar, can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys. When the blood vessels get damaged, they don’t work properly so that many people with diabetes develop high blood pressure, which can damage kidneys. Diabetic kidney disease is defined as macro albuminuria (albumin to creatinine ratio [ACR] >35 mg/mmol [400 mg/g]), or micro albuminuria (ACR 3.5-35.0 mg/mmol [35-400 mg/g]) associated with retinopathy (type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes) and/or >11 years' duration of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). In most patients with diabetes, chronic kidney disease can be attributable to diabetes mellitus if these criteria are met. Other causes of diabetic kidney diseases should be considered in the presence of any of the following circumstances: rapidly decreasing GFR, absence of diabetic retinopathy, presence of active urinary sediment, or signs or symptoms of other systemic disease. The diagnosis is most of the time conclusively made by kidney biopsy, though it is rarely necessary.
-
Non-diabetic kidney disease
-
Renal tract obstruction
-
Multiple myeloma
-
Use of drug therapies for glycaemic control
-
Diabetes inspidus
Track-11: Kidney and Bladder stones
Kidney or bladder stones area unit solid build-ups of crystals made of minerals and proteins found in excretory product. Bladder diverticulum, enlarged prostate, bladder disorder and tract infection will cause an individual to have a greater chance of developing bladder stones. But if a stone irritates the bladder wall or blocks the flow of urine, signs and symptoms may include such as Lower abdominal pain during urination, frequent urination. Difficulty urinating or interrupted urine flow, blood in the urine, cloudy or abnormally dark-coloured urine. Bladder stones begin to grow once excretory product is left within the bladder after urinating. This is usually because of an underlying medical condition that stops the bladder from completely emptying when using the toilet.
-
Abdominal and pelvic CT
-
Intravenous pyelogram
-
Xanthine stones
-
Calcium phosphate stones
-
Nephrostomy
-
Calcium stones
-
Uric acid stones
-
Cystine stones
-
Struvite stones
Track-12: Surgery for Renal Disease
Nephrectomy is the surgical removal of a kidney, performed to treat variety of urinary organ diseases together with kidney cancer. It is conjointly done to remove a healthy urinary organ from a living or deceased donor, once a part of a urinary organ transplant procedure. The phases of kidney disease are controlled by the glomerular filtration rate and by this process the kidneys filter the blood, removing excess wastes and fluids. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) may be a calculation that determines however well the blood is filtered by the kidneys. They are Acute kidney disease is the sudden loss of kidney function that happens when high levels of waste products of the body's metabolism accumulate in the blood. Chronic nephropathy may be a steady advancement of lasting urinary organ ill that exacerbates over varied years. Pediatric nephropathy will influence kids in numerous ways that, going from treatable disorders without long term outcomes to life-threatening conditions. Polycystic Kidney Disease is characterized by the development of numerous kidney cysts, which cause variations in both the kidney structure and function.
-
Partial nephrectomy
-
Radical nephrectomy
-
Bilateral nephrectomy
-
Laparoscopic Surgery
-
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy
-
Regional lymphadenectomy
-
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
-
Renal hypertension
Track-13: Biomarkers of Kidney Diseases
Kidney bio-markers include serum creatinine (sCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), urinary albumin/protein and volume excretion. However, sCr or BUN cannot distinguish injury from hemodynamic changes in the kidney that lead to appropriate changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), particularly when the changes are acute. At present, serum creatinine, which is used to calculate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), is the most commonly used marker of renal function. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) remains the perfect marker of excretory organ operates. Other bio markers like proteinuria might precede excretory organ operate decline and have incontestable to possess robust associations with illness progression and outcomes.
-
Urinary angiotensinogen
-
Urinary microRNA
-
serum creatinine
-
Blood urea nitrogen
-
Cystatin C
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine
-
β-trace protein
Track-14: Cardiovascular Impacts of Kidney Diseases
Heart failure, affects the kidney through the backward and the forward failure effects. Systemic Venous congestion results in an increase in the capillary pressure, transudation into interstitial spaces with decrease in effective circulating volume. In addition, underlying conditions that cause renal disease, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, put people at risk for cardiovascular disease. Patients with chronic kidney disease are at considerably increased risk for cardiovascular disease and sudden cardiac death. One mechanism underlying increased cardiovascular risk in patients with renal failure includes over activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Multiple human and animal studies have shown that central sympathetic outflow is inveterately elevated in patients with each end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
-
Anemia
-
Diabetes
-
High blood pressure
-
High homocysteine levels
-
Calcium-phosphate levels
Track-15: Stem Cells in Renal Disorders
Bone marrow stem cells, including hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells can also participate in the repair process by proliferation. The reno protective potential of pluripotent and adult stem cell therapy of acute and chronic kidney injury are based on stem cell-induced kidney regeneration. Specifically, cell engraftment, incorporation into renal structures, or paracrine activities of embryonic or induced pluripotent stem cells as well as mesenchymal stem cells and renal precursors are analysed. Various sorts of stem cells will restore nephritic operate in diagnosing models of acute and chronic excretory organ injury. Researchers are examining how stem cells may help kidneys to repair harmed nephrons and re-establish kidney function. Scientists are contemplating how the kidney can recover itself and what sorts of kidney cells are associated with this procedure.
-
Embryonic
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell
-
Adult stem cell therapy
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
-
Cell engraftment
Track-16: Renal Nutrition and Metabolism
Renal nutrition is concerned with the special nutritional needs of kidney patients. Renal nutrition is concerned with ensuring that kidney patients eat the proper foods to form chemical analysis economical and improve health. Renal Nutrition may be outlined as a diet recommended in chronic renal failure and that is meant to manage the consumption of macromolecule, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, and fluids. Because the kidneys of individuals on dialysis are incapable to cope with excess fluid and different metabolic wastes.
Metabolism is the chemical reactions involved in retaining the dwelling nation of the cells and the organism. Metabolism can be quite simply divided into classes:
Catabolism - the breakdown of molecules to get energy
Anabolism - the synthesis of all compounds required through the cells.
-
Blood urea nitrogen
-
Protein equivalent of nitrogen appearance (PNA)
-
Renal osteodystrophy
-
Nutritional therapy
-
Anemia and erythropoietin
-
Hypelipidemia
Track-17: Glomerular Disorders
Glomerular disorders occur by itself or could also be related to an underlying medical condition that affects alternative organ systems, like lupus, diabetes, or sure infections. Glomerular sickness will develop suddenly (called Acute), or develop slowly over an amount of years (called Chronic). Treatment of glomerular disorder depends upon its cause and sort. Many diseases affect kidney function by attacking the glomeruli, the small units inside the excretory organ wherever blood is clean. Glomerular diseases damage the glomeruli, permitting macromolecule and typically red blood cells drip into the urine.
-
Glomerulonephritis
-
Glomerulosclerosis
-
Bacterial endocarditis
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
-
Membranous nephropathy
Track-18: Renal Replacement Therapy
Renal replacement therapy (RRT) is the therapy that replaces normal blood-filtering function of the kidneys. It is used once the kidneys don't seem to be operating well that is termed renal failure and includes acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. Renal replacement medical aid includes dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis), hemofiltration, and hemodiafiltration, that measure numerous ways of filtration of blood with or while not machines. Renal replacement medical aid conjointly includes kidney transplantation, that is that the final variety of replacement in this the previous kidney is replaced by a donor kidney.
-
Peritoneal dialysis (PD)
-
Intermittent hemodialysis (IHD)
-
Continuous renal replacement therapies (CRRT)
-
Continuous hemofiltration (CHF)
-
Continuous hemodialysis (CHD)
-
Continuous hemodiafiltration (CHDF)
-
Intermittent renal replacement therapy (IRRT)
-
Intermittent hemodiafiltration (IHDF)
Track-19: Kidney Transplantation
A kidney transplant is a surgical method that’s done to treat Kidney Failure. This surgery is a lifesaving choice for thousands of patients with end stage renal disease. Kidney transplantation or renal transplantation is that the surgical operation of a kidney into a patient with end-arrange kidney diseases. Kidney transplantation is often named deceased donor called living donor or cadaveric transplantation relying upon the wellspring of the giver organ. Living donor kidney transplants are formerly differentiated as non-related living transplants or, living related transplants contingent upon whether a biological relationship exists between the kidney donor and kidney recipient.
-
Renal transplantation in obese patients
-
Kidney biopsy
-
Proteinuria
-
Kidney transplantation recipients
-
Living donors of kidney
-
Post-transplant lympho-proliferative disorder
-
Transplantation rejection
-
Artificial kidney
Track-20: Nephrology Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic imaging may be a strategy and procedure of constructing the visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and demonstrative intervention. The treatment for renal disorder differs depending on what phase the renal disorder is and alternative individual factors. For those whose kidneys no longer function well enough on their own without renal therapy, specialist will typically recommend either renal dialysis or a kidney transplant. Nephrological treatment consists of steroid medications, blood products, plasma exchange and dialysis. Kidney complications will have important impact on quality and length of life, and then psychological support, health education and advanced care coming up with play key roles in nephrology.
-
Diagnostic imaging
-
Chronic peritoneal dialysis
-
Percutaneous cannula placement
-
Renal scintigraphy
-
Dialysis
-
Transplantation
-
Medical ultrasonography
-
Computed axial tomography
-
Renal arteriography
World Kidney Congress 2020 conference is the leading event which rotates between continents and is organized in collaboration with regional nephrology societies with the innovative theme “Investigating the Current Novelty & Core Approaches in Kidney Disorders and Nephrology”. This conference highlights on the topics related to nephrology, kidney disorders, pediatric nephrology, geriatric nephrology, hereditary kidney diseases, dialysis, urology & urinary tract infections, onco-nephrology and nephritis, kidney and bladder stones, renal replacement therapy, kidney transplantation and recent advancements in nephrology diagnosis and treatment.
Summary:
World Kidney Congress deals with study of kidneys as well as its diseases like normal kidney function, kidney problems, the treatment of kidney stone problems and renal replacement therapy, CKD which are common like haemodialysis and kidney transplantation. Kidney function studies: increased levels of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine are the hallmarks of acute renal failure. Not only this innovative conference will enhance your practical and theoretical knowledge, but it will also provide you with the unique opportunity to meet and network with a wide range of professionals in the field of nephrology and for its recent approaches.
Global Market Analysis on Renal Disorders:
In 2009, 7.5% of qualitative analysis patients were treated with PD; by 2016, the data point had inflated to ten.0%. And according to the United States Renal Data System & 10.5% of dialysis patients with new Medical Evidence Report were treated with PD. Although metallic element could be a nice modality for several patients, clinical complications like tube malfunctions, peritonitis, and ultrafiltration failure do occur, and lead some patients to transition from PD to hemodialysis (HD). According to knowledge bestowed at ASN urinary organ Week 2018, on the brink of one in six patients United Nations agency started on metallic element in 2015 had switched to HD among one year of initiation. With a growing share of incident qualitative analysis patients treated with metallic element, and a stable rate of conversion from PD to HD, at least during the first year of PD, the net result is that the amount of patients switch from metallic element to HD is steady increasing. During 2015, almost 12,000 patients switched from metallic element to HD.
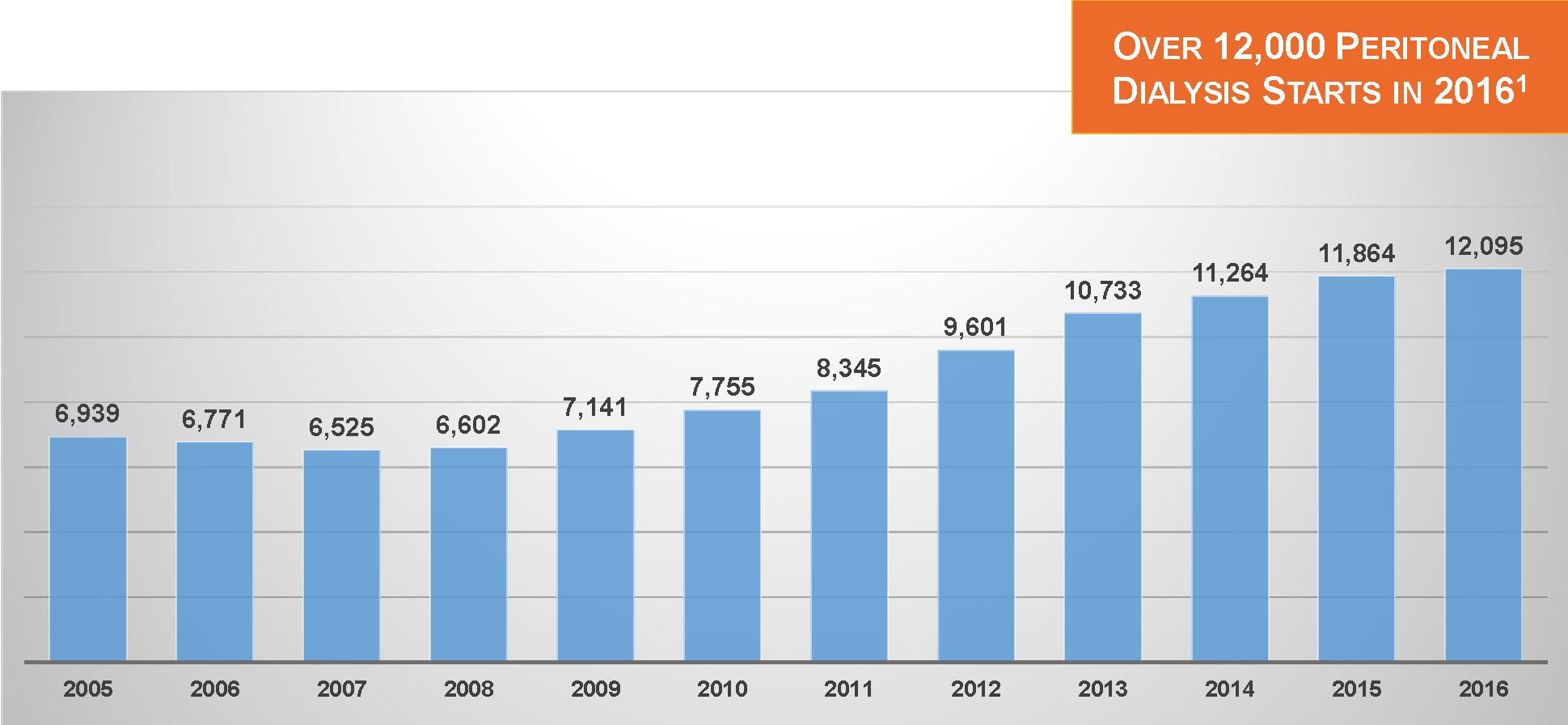
Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Market Analysis:
End-stage renal disease (ESRD), also known as kidney failure, is the last stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD). During ESRD/CKD, kidneys lose their filtering ability, making dialysis a primary mode of treatment. Globally, around 2 million people are affected with ESRD each year.
According to the US Renal Data System’s 2018 Annual Report, as of December 2016, there were 124,675 newly reported cases of ESRD; 63.1% of prevalent ESRD patients received hemodialysis (HD), and 7.0% were treated with peritoneal dialysis (PD). According to the International Society of Nephrology, 1 out of 3 people in the general population is at an increased risk of CKD, with the global estimated CKD prevalence worldwide varying from 11% in North America and 12% in Europe to as low as 7% in South Asia and 8% in Africa. The growing patient population for ESRD may be a major issue driving the expansion of the chemical analysis market.
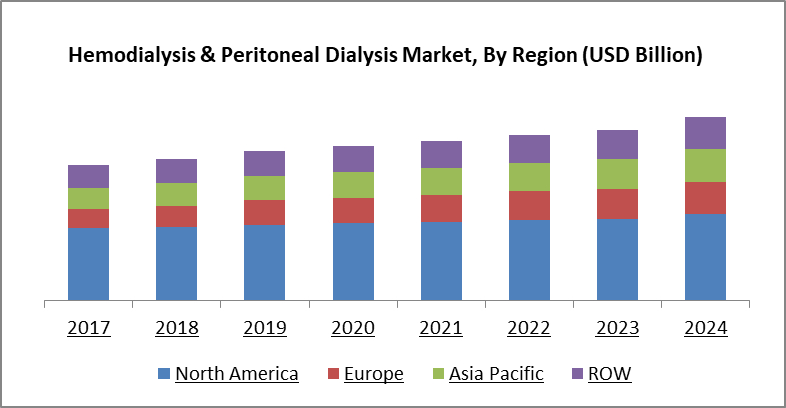
The Asia Pacific is one of the major revenue-generating regions in the hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis market. China, India, and Japan are the major countries responsible for the high growth of this regional market owing to factors such as the increasing per capita income, improving healthcare infrastructure, and supportive government activities in these emerging countries. Furthermore, the increasing geriatric population, the growing incidence of ESRD, and the rising acceptance of home hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are also driving the growth of this regional market.
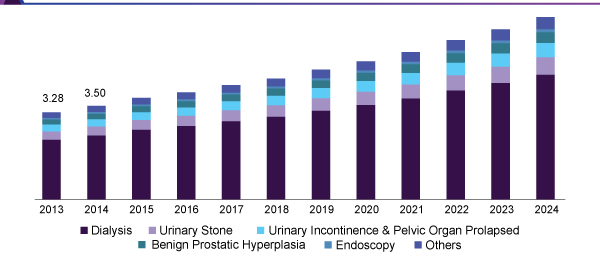
Nephrology and Urology Devices Market Analysis:
The global medical specialty and urogenital medicine devices market size was calculable at USD 18.03 billion in 2016 and is anticipated to develop at a CAGR of 7.1% over the forecast amount. Increasing prevalence of kidney failure and end-stage renal diseases has resulted in clinical urgency for devices that can improve existing patient outcomes and curb long-term costs associated with treatment of kidney diseases.

Universities which are dealing with Kidney and Nephrology Research Worldwide:
- United Arab Emirates University
- University of Strasbourg (Strasbourg, France)
- Columbia University (New York, NY, USA)
- Imperial College London Diabetes Centre (UAE)
- New York University (UAE)
- Gulf Medical University (UAE)
- University Udayana (Indonesia)
- Harvard University (Cambridge, MA, USA),
- Oxford University (Oxford, UK)
- Yale University (New Haven, CT, USA)
- McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada)
Societies Associated which are dealing with Diabetic and Metabolic Diseases Research World:
- International Society of Nephrology (ISN)
- American Society of Nephrology (ASN)
- Indian Society of Nephrology
- Canadian Society of Nephrology (CSN)
- Hong Kong Society of Nephrology (HKSN)
- The Renal Association
- Australian and New Zealand Society of Nephrology (ANZSN)
- Malaysian Society of Nephrology (MSN)
- National Kidney Foundation (NKF)
- Saudi Society of Nephrology and Transplantation (SSN&T)
- Spanish Society of Nephrology
- Spanish Dialysis and Transplant Society
- Spanish Dialysis Foundation
- Danish Society of Nephrology
- Swedish Society of Nephrology
- British Association of Pediatric Nephrology
- French Society of Nephrology
- Polish Society of Nephrology
- Albanian Society of Clinical Nephrology
- Belgian Society of Nephrology
Hospitals and Research Clinic which are dealing with Nephrology and Kidney Diseases Research Worldwide:
- Cleveland Clinic Dubai
- Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN),
- Massachusetts General Hospital (Boston, MA)
- Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, OH)
- Johns Hopkins Hospital (Baltimore, MD)
- Addenbrooke’s Hospital – Cambridge, Barnet General Hospital (UK)
- Cygnet Hospital Beckton (UK)
- Wooridul Spine Hospital-Seoul (South Korea)
- BIMC Hospital- Nusa Dua (Indonesia)
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute (India)
Conference Highlights
- Nephrology
- Kidney Disorders
- Pediatric Nephrology
- Geriatric Nephrology
- Clinical Nephrology
- Hereditary Kidney Diseases
- Dialysis
- Urology & Urinary Tract Infections
- Onconephrology and Nephritis
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Kidney and Bladder Stones
- Surgery for Renal Disease
- Biomarkers of Kidney Diseases
- Cardiovascular Impacts of Kidney Diseases
- Stem Cells in Renal Disorders
- Renal Nutrition and Metabolism
- Glomerular Disorders
- Renal Replacement Therapy
- Kidney Transplantation
- Nephrology Diagnosis and Treatment
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 22-23, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Nephrology & Therapeutics
- Journal of Transplantation Technologies & Research
- Journal of Molecular Biomarkers & Diagnosis
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by